Different VPN Types and Protocols (Tunnels) – VPNs Explained
- July 29, 2021
- 11 minutes Read
- VPN Service
Have you ever wondered how your data remains secure while you browse the internet? The answer lies in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). Online privacy is paramount in this digital age, so understanding VPN types and protocols is crucial.
How does it all work together and how does a VPN protect you from hackers and cyberthreats? VPNs establish a secure connection between your device and a remote server, encrypting your data in transit. There are several types of VPNs available, each with its own features and protocols.
Here are some of the major types of VPNs:
- Remote-access VPN
- Site-to-site VPN
- Personal VPN
- Mobile VPN
- Cloud VPN
- SSL VPN
There are various types of VPNs, each serving distinct purposes. From the versatility of remote access VPNs to the enhanced security of site-to-site VPNs, the options are vast.
Secure VPN connections are made through secure protocols like OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, and IKEv2/IPsec. In order to protect your data, these protocols utilize encryption techniques and authentication procedures.
Also, there is another major type of VPN available, like an Extranet-based VPN.
What Is a VPN and How Does It Work?
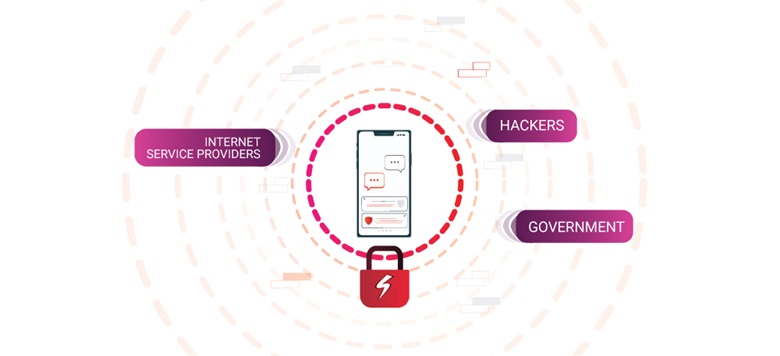
A VPN is a type of service that lets you connect your device to the internet in a secure and encrypted way. This means you can surf the web without worrying about your data being tracked or accessed.
The connection acts as a tunnel for your internet traffic, making it harder for third parties, such as hackers, Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and even governments, to access and decrypt your data.
VPN works by routing a device’s internet connection through a chosen VPN’s private server instead of the internet service provider (ISP). This implies that when data is transmitted to the internet, it comes from the internet rather than the computer.
VPN creates a private secure “tunnel” from the device to the internet and hides all the data, popularly referred to as encryption. When using a VPN, encryption ensures that your information is kept private from hackers and other threats.
Encryption encrypts data so that it can’t be read without the use of a strong password called a key. The key’s purpose is to decrypt the complex code into which the data has been encrypted. Only the key can be recognized by the computer and by the VPN server at the same time.
Decryption is the act of decrypting data by a computer and by a VPN server. Decryption makes the encrypted data readable again through a vital application. Various types of VPN use different types of encryption techniques. By using a VPN, you are assured of your privacy and can use the internet as you wish, knowing that your information is safe.
6 Different Types of VPNs

Now let’s have a look at the detailed discussion of the different types of VPNs. The most used type of VPN is personal VPN like express, nord vpn, IPVanish.
1. Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPN also known as Corporate VPN enables users to connect to a private network and remotely access their services and resources. Internet connections between the user and the private network are completely secure and confidential. Remote Access VPN is beneficial for both business and home users.
This VPN allows employees of a company who travel out of the station to connect to their company’s private network and access files and resources remotely. For private users, VPN services can be used to break regional restrictions on the internet and can also make it possible to access blocked websites.
Good access, Fortinet, and Pure VPN are examples of Remote Access VPNs.
2. Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-site VPN is a type of VPN that connects two or more networks, such as a corporate network and a branch office network, securely over the internet. They are commonly used in large companies and are known as Router-to-Router VPN.
It is ideal when several devices need to be protected to preserve every device connected to the router. Site-to-Site VPN can be used by businesses that have offices in different locations for the purpose of securing the networks of all offices.
When several offices of the same company are connected using a Site-to-Site VPN, it is called, Intranet Based VPN. Conversely, when companies use a Site-to-Site VPN to connect to the office of another company, it is known as Extranet Based VPN.
Site-to-Site VPN creates a kind of invisible bridge between offices situated at different locations and connects them through the internet and, at the same time, enables secure and private communication among various networks. Cisco’s Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) and Nokia provide instructions for setting up a VPRN service.
3. Personal VPN
Homes and small businesses commonly use standalone or personal VPN. It uses an application that creates an encrypted private connection from your device to the VPN servers. Personal VPNs are ideal for private use because they do not require complex setup or configurations. Here are some examples of Personal VPN Services:
4. Mobile VPN
Some VPNs function as browser extensions or add-ons. This can be described as an add-on to browsers such as Google Chrome or Firefox. For example, Opera App comes with an in-built VPN. But the shortfall of this is that data can only be protected when using that particular browser, which means that other Apps will not be protected.
5. Cloud VPN
A Cloud VPN is a type of VPN that provides VPN services through a cloud-based network infrastructure. It enables users to securely access a company’s applications, data, and files in the cloud through a website or via a desktop or mobile application.
Cloud VPNs provide globally accessible VPN access to end-users through a cloud platform, making it easy to deploy and manage. Cloud VPNs are available in a number of different form factors and provide several benefits compared to traditional site VPNs.
Cloud VPNs are different from other types of VPNs, such as remote access VPNs or site-to-site VPNs. Cloud VPNs provide a cloud-based network infrastructure that delivers VPN services, while other types of VPNs provide secure connectivity between individual devices or networks.
6. SSL VPN
An SSL VPN is a secure way for devices with internet access to connect remotely to a corporate network. It uses the SSL or TLS protocol to encrypt data between the device and the SSL VPN server. This type of VPN can be easily set up using only a web browser and is commonly used by businesses for remote and network-level access.
6 Most Popular and Secure VPN Protocols

The VPN protocol is the type of technology the VPN service uses to ensure that the fastest and safest VPN connection to the internet is achieved. When encryption standards and transmission protocols are combined, the VPN protocol determines how data is transmitted between the device and the VPN server.
The most popular VPN protocol being used are:
1. WireGuard Protocol
WireGuard is an industry-leading connection protocol that provides the best security and speed for every VPN need. It’s overall best for anything like gaming, streaming, secure file transfer (FTP), bypassing geo-blocks/strict firewalls, etc.
2. Openvpn Protocol
OpenVPN is the best for its security, speed, and reliability. Since it is open source, anyone can modify and use it, whether individuals or businesses. People who need the best security use OpenVPN for personal and business use. It is, however, not ideal for gaming because of its high latencies.
3. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is a type of network tunneling that was originally created for early VPNs. Basically, it lets you create a secure way to send data from a remote server to a server in your private enterprise network by creating a VPN over a TCP/IP network. Modern devices no longer support the PPTP protocol by default due to its security issues.
4. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP/IPSec)
This combination of L2TP and IPSec protocol was founded by CISCO hardware networking company. L2TP provides a direct tunnel for layer 2 traffic and communication, while IPSec provides encryption and authentication.
5. Internet Key Exchange Protocol (IKEv2)
IKEv2 is an upgraded and new version of L2TP. It provides a secure, authenticated communication channel between two parties. IKEv2 offers good security, speed, and less bandwidth consumption, making it ideal for online games. Moreover, it’s extremely stable and improves gaming performance by reducing lag spikes.
6. Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
SSTP is a highly secure VPN protocol that uses SSL/TLS encryption to protect data in transit. SSTP can bypass most firewalls and proxy servers, making it a good choice for users accessing restricted content. Windows users often choose SSTP because it is easy to set up and use.
Is VPN Legal and Safe to Use?

You can use VPNs legally and safely in some countries, while they are strictly forbidden in others. As such, you should always adhere to your country’s rules and regulations before using a VPN.
In North America and Western Europe, VPNs are legalized. VPNs may not be illegal in other countries, but they may be strictly regulated and censored. For example, no business can use a VPN in China without obtaining a license. In Russia, only government-approved VPNs are allowed.
All major social media platforms are blocked in Pakistan. However, Symlex VPN can unblock social media in countries like Uzbekistan, Pakistan, etc.
In some countries, the use of VPN is strictly prohibited. This is the case in countries like North Korea, Belarus, etc. The country’s laws may also require VPN providers to keep records of the internet traffic of the VPN companies.
This means that the information of the VPN users might be stored and may even be used by the VPN provider for unauthorized purposes. As a result, it becomes essential that a potential VPN user reads and understands the terms of use of any VPN service.
It is also advised that a VPN user should opt for a paid VPN instead of a free one. This is because many free VPNs lack strong encryption, some may not even offer proper data encryption, and data logging is quite common in most cases. In extreme cases, some companies may sell the user’s data to third parties and advertisers.
How Do You Choose a VPN?
It is important to consider several factors when choosing a VPN to ensure you are selecting the right one. Here are some crucial factors to consider:
- Security: Ensure your VPN has strong encryption (e.g., AES-256) and robust security protocols (e.g., OpenVPN/IKEv2).
- Speed & Reliability: Make sure that your VPN service is fast and reliable. It is important to choose a VPN that does not slow your internet connection.
- Supported VPN Protocols: Consider the protocols the VPN provider supports. Common protocols, such as OpenVPN/IPSec /L2TP/SSTP, etc., should be considered.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure your VPN is compatible with Windows, Mac/iOS/Android devices. Depending on the VPN provider, some may support multiple platforms.
- Customer Support: A VPN provider’s customer support can be important if you have any questions or need help with your VPN service.
- Cost: Consider how much it’ll cost to use a VPN service and ensure it’s within your means. Different VPNs have different pricing options, so compare features and prices to get the best bang for your buck.
These key factors will help you to select your desired VPN. If you’re a gamer, you should look for a VPN with game-centric features and a wide range of protocols. If you want to secure yourself online, choose a VPN with the best security and speed.
FAQs
Which is better: IKEv2 or IPSec or L2TP?
IKEv2 is better than L2TP regarding speed, security, and compatibility. L2TP is a combination of two protocols, L2TP and IPSec. L2TP establishes the tunnel for data transmission, and IPSec secures the communication between the devices.
Which is better: SSL or IPsec VPN?

Organizations must consider their unique needs when choosing between SSL VPNs and IPsec VPNs. IPsec VPNs allow full network access and are suited for site-to-site use but are complex and costly. SSL VPNs offer precise control, ideal for remote access and web apps. Both come with their own advantages and disadvantages, so choose wisely.
Final Words
VPNs are the way to go if you want to keep your online data safe and secure. We’ve looked at different types of VPNs and how they work, but VPNs create a tunnel for your data to go through, keeping it from being seen by anyone.
When you’re diving into the VPN world, make sure you pick the right protocol for your needs – security, speed, compatibility, and so on. Meanwhile, you can also check out another write-up on the best VPN protocol for gaming.





